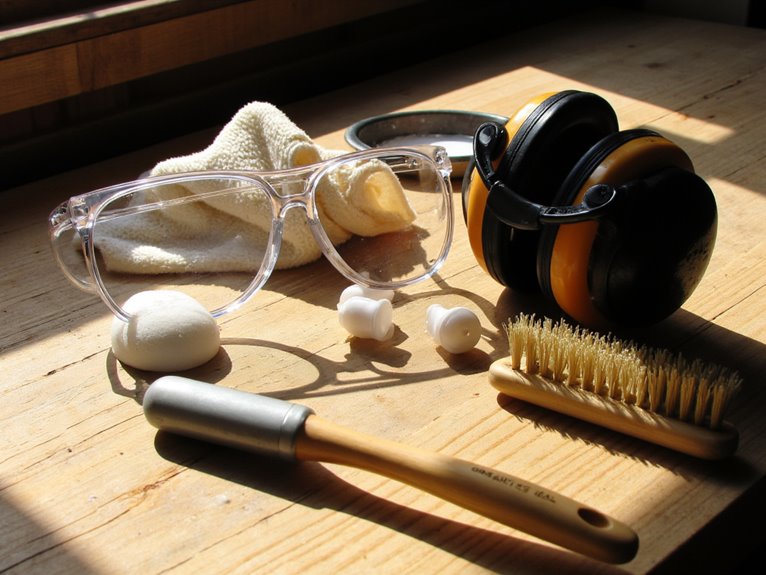
Tips for Maintaining and Cleaning Your Hearing and Eye Protection Gear
You should clean your hearing and eye protection with soft brushes and mild soap, avoiding harsh chemicals that degrade materials. Air-dry equipment completely before storing in well-ventilated areas to prevent mold growth. Inspect gear before each use for cracks or deformation, replacing foam inserts and ear cushions every six months. Remove PPE in reverse order, handling contaminated items first. Replace disposable earplugs after single use and damaged lenses immediately. Continue below for thorough maintenance protocols.
We are supported by our audience. When you purchase through links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission, at no extra cost for you. Learn more. Last update on 26th December 2025 / Images from Amazon Product Advertising API.
Notable Insights
- Clean equipment with warm water and mild soap using soft brushes or microfiber cloths, avoiding harsh chemicals.
- Air-dry all components completely before storage to prevent mold and bacterial growth in well-ventilated areas.
- Inspect gear before each use for cracks, tears, or deformation and maintain detailed logs of replacements.
- Replace foam earplugs after each use and earmuff cushions every six months or when damaged.
- Store equipment in dedicated containers at cool temperatures away from heat sources that warp materials.
Proper Cleaning Techniques for Optimal Performance
While proper maintenance extends the life of your hearing and eye protection gear, regular cleaning directly impacts their performance and safety effectiveness. You’ll need a soft brush or microfiber cloth to remove surface debris, plus warm water with mild soap for deeper cleaning. Avoid harsh chemicals that cause material degradation to plastics and electronics.
Your cleaning frequency should align with usage patterns. Remove padding following manufacturer instructions before washing in soapy water, then air-dry completely.
Clean protective gear padding regularly based on how often you use it, following proper washing and drying procedures.
For non-removable components, use damp cloths without soaking materials. Cotton swabs reach tight seams effectively. Never wet foam earplugs—replace them instead.
Keep liquids away from microphones and electronic components to prevent malfunction. Always wash hands before handling any gear to prevent skin oils and debris from transferring to the equipment. Regular inspection identifies cracks or tears requiring immediate replacement. Store your gear in a cool, dry place away from sunlight to prevent material deterioration and extend its lifespan.
Storage and Drying Best Practices
After cleaning your hearing and eye protection equipment, proper storage and drying becomes critical for maintaining gear effectiveness and preventing contamination.
Complete air drying prevents mold and bacterial growth that compromises device performance. Place equipment on clean, absorbent surfaces in well-ventilated areas away from direct sunlight. Heat sources like hair dryers warp plastic components and degrade foam materials.
Effective moisture management requires dedicated storage containers designed specifically for protection gear. Avoid humid locations, pockets, or bags where crushing occurs. Store earplugs in a clean, dry container to maintain hygiene and prevent contamination between uses.
Specialized drying techniques include hearing aid dryers with desiccants that absorb moisture overnight. UV light devices simultaneously sanitize and dry equipment. For rechargeable units, use charging stations with integrated drying functions. Open battery doors overnight to allow air circulation and prevent moisture buildup in electronic components.
Maintain storage areas with low humidity and cool temperatures to prevent material degradation and extend equipment lifespan.
Regular Inspection and Maintenance Schedules
Since protection gear degrades through normal use, establishing a systematic inspection routine prevents equipment failure when you need it most.
Perform visual checks before each use, examining ear cushions, headbands, and lenses for cracks, tears, or deformation. Look for stretched headbands that compromise seal integrity and dirt buildup that reduces comfort.
Schedule component replacements at least twice yearly for ear cushions and foam inserts. Replace entire units when headbands lose elasticity.
Test electronic hearing protectors’ amplification functions according to manufacturer specifications. Verify noise reduction ratings after cleaning or part replacement.
Set maintenance reminders to track performance over time. Document all inspections and replacements in detailed logs.
- Inspect foam liners for hardness or brittleness requiring immediate replacement
- Conduct seal checks after maintenance to confirm no air leaks compromise protection
- Test eye protection lenses for scratches that reduce visibility
Safe Handling and Usage Guidelines
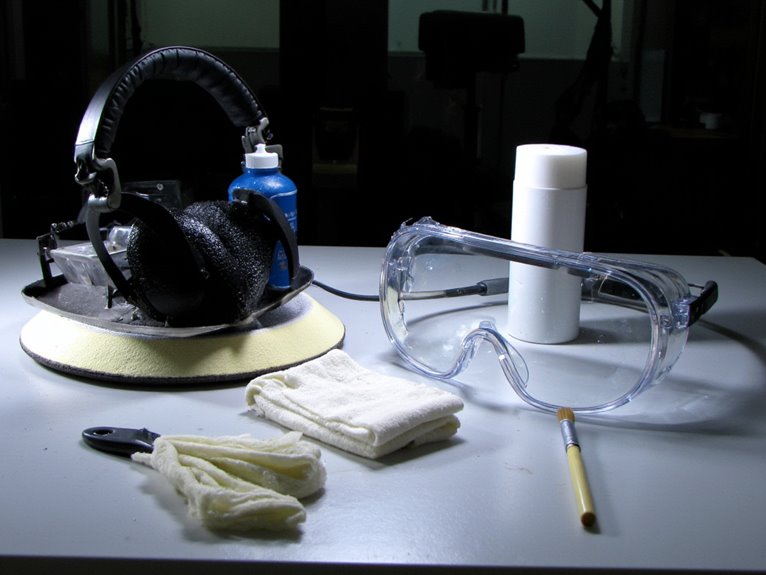

Following manufacturer protocols for donning and doffing personal protective equipment prevents contamination and guarantees maximum protection effectiveness.
Start with clothing, then respiratory protection, eye protection, head protection, and finally gloves. This systematic approach minimizes contamination risks during equipment changes.
Remove PPE slowly in reverse order, handling the dirtiest items first. Never touch common objects while wearing contaminated gear. In emergency situations, prioritize removing the most hazardous contaminants first before exiting the area.
Ensure proper fit for both hearing and eye protection. Devices must provide maximum coverage without gaps.
Clean your hands thoroughly before handling reusable earplugs to prevent bacterial contamination. Always inspect covered skin areas after PPE removal and clean any exposed residue immediately to maintain safety standards.
For construction workers, custom-fit earplugs offer a discreet and lightweight solution that requires proper maintenance to ensure optimal noise reduction performance.
Replacement Strategies and Hygiene Management
Maintaining peak protection performance requires establishing systematic replacement schedules and rigorous hygiene protocols for both hearing and eye protection equipment.
You’ll need to replace disposable earplugs after each use, while reusable plugs require replacement when they lose pliability or show damage. Earmuff cushions and foam inserts need replacement every six months or when hardened. For eye protection, replace lenses immediately if scratched or cracked to maintain optical clarity.
Contamination prevention demands regular cleaning with manufacturer-approved solutions and proper storage in clean, dry cases.
Proper contamination control requires consistent cleaning with approved solutions and secure storage in moisture-free protective cases.
Clean reusable earplugs with warm, soapy water and disinfect earmuff surfaces after each use. Replacement intervals should follow manufacturer guidelines while accounting for usage intensity and environmental exposure conditions. Custom molded earplugs can be easily remolded if they become damaged or lose their original fit.
- Establish routine weekly inspections to identify worn components before they compromise protection
- Never share personal protective equipment to prevent cross-contamination and infection transmission
- Document replacement dates to track equipment lifecycle and optimize replacement intervals
On a final note
You’ve got the tools and knowledge to maximize your hearing and eye protection equipment’s lifespan. Don’t skip daily cleaning routines or monthly inspections—they’re critical for maintaining ANSI Z87.1 and NIOSH certification standards. Replace foam earplugs after single use and safety glasses when transmittance drops below 85%. Store gear in clean, dry environments between 32-100°F. Following these protocols guarantees ideal protection performance and extends equipment service life considerably.