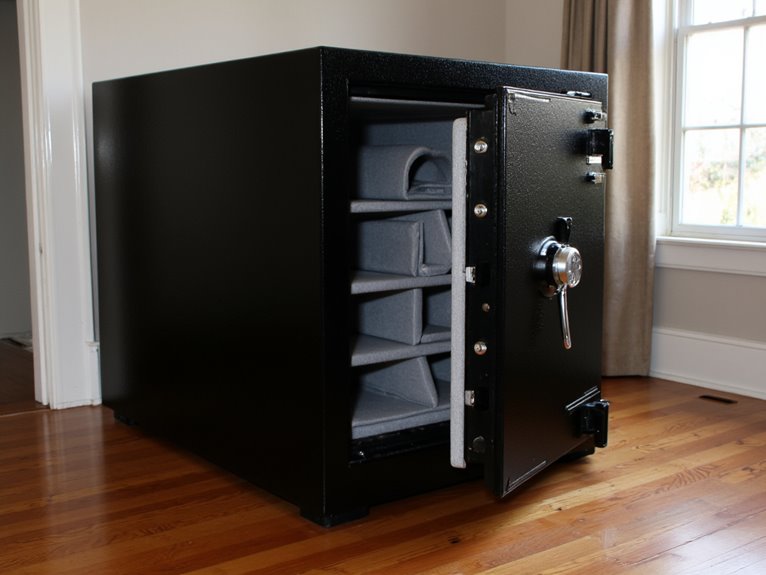
Top Features to Look for in a Home Safe
When choosing a home safe, you’ll want to prioritize these essential features: robust locking mechanisms like biometric or dual-lock systems, steel construction with at least 10-gauge thickness, certified fire resistance ratings of 1-2 hours, waterproof seals for flood protection, adjustable interior shelving for organization, and secure mounting options. Look for UL or EN certification standards, reliable power management with battery backup, and extensive warranty coverage. Advanced features like motion detection and smartphone integration enhance security further, and exploring these specifications thoroughly will help you make the most informed investment decision.
We are supported by our audience. When you purchase through links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission, at no extra cost for you. Learn more. Last update on 29th December 2025 / Images from Amazon Product Advertising API.
Notable Insights
- Choose electronic or biometric locks for faster access, or dual lock systems for maximum security protection.
- Ensure steel walls are at least 3/16″ thick with higher gauge ratings for better cutting and drilling resistance.
- Look for certified fire ratings of 30 minutes to 2 hours that maintain internal temperatures below 350°F.
- Select interior dimensions and adjustable shelving that accommodate your specific valuables and organizational needs.
- Verify reliable power management with battery backup and physical override keys for emergency access situations.
Locking Technology Options and Security Standards
When selecting a home safe, the locking mechanism serves as your primary barrier against unauthorized access and determines both security level and daily usability. Your lock selection criteria should prioritize both convenience and protection.
Key locks offer simplicity but risk key loss or duplication. Mechanical combination locks provide battery-free reliability with slower access times. Electronic locks deliver programmable codes and faster entry while requiring power sources.
Each locking mechanism balances convenience against security, requiring careful consideration of access speed, reliability, and vulnerability to common threats.
Biometric locks use fingerprint recognition for keyless convenience and exclusive access. Dual lock systems combine two mechanisms for enhanced security, common in Euro Grade 6-7 safes. UL-rated locks indicate tested resistance against attacks.
For user access management, electronic systems excel with multiple programmable codes, audit trails, and time delay functions. Higher-grade safes incorporate slip-clutch mechanisms and over-center cam technology for superior manipulation resistance. Tamper-resistant locks increase resistance to manipulation and provide enhanced security against unauthorized entry attempts. Safe locks feature interchangeable mounting dimensions that allow for lock upgrades and replacements without requiring safe modification. Traditional combination locks feature rotating dial mechanisms that eliminate the need for batteries or complex digital components.
Construction Materials and Wall Thickness
When you’re selecting a home safe, the construction materials and wall thickness directly determine your protection level against both fire damage and forced entry attempts.
Steel grade selection starts with the outer shell, where 12-gauge steel (0.105 inches thick) provides basic protection, while premium safes use 10-gauge steel (0.134 inches thick) or thicker for enhanced security ratings.
Your safe’s wall thickness should include high-strength concrete fill with a minimum PSI of 6,300 for TL-15 rated protection, creating walls that range from 2 inches for basic models to over 6 inches for maximum security applications. Advanced fire-resistant materials like DryLight® offer superior protection while being 19% lighter than traditional drywall insulation, allowing manufacturers to incorporate thicker steel layers without excessive weight. Intumescent coatings can be applied to steel components to expand under high temperatures and create an insulating barrier that shields the safe’s contents from direct heat exposure.
Steel Grade Selection
The steel grade you select directly determines your home safe’s ability to withstand attack and environmental conditions over time. Steel quality affects resistance to cutting, drilling, and prying attempts. A36 steel serves as the industry standard for basic protection, while GR80 delivers superior metal durability through higher tensile strength.
| Steel Grade | Tensile Strength | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| A36 | 58,000-80,000 psi | Non-TL rated safes |
| GR80 | 100,000+ psi | TL-15, TL-30 safes |
| Galvanized | Varies by base grade | Corrosion resistance |
GR80’s superior strength allows manufacturers to use thinner plates without compromising security, reducing overall weight. This high-strength steel meets UL requirements for advanced ratings. Consider galvanized options for humid environments where corrosion resistance matters.
Optimal Wall Thickness
Beyond steel grade selection, wall thickness determines how long your safe can withstand sustained attacks from cutting tools, drills, and prying equipment.
Most residential safes feature walls ranging from 3/16″ to 1/2″ thick, balancing protection with manageable weight for home installation.
The ideal thickness depends on your security requirements and practical constraints. Basic safes use 14-gauge steel (0.0747 inches), while high-security models employ up to 1-inch solid steel walls.
Doors typically exceed wall thickness, sometimes reaching 1.5 inches to resist forced entry attempts.
Thicker walls reduce flexibility, making deformation and prying attacks considerably more difficult.
However, increased thickness adds substantial weight, complicating delivery and placement.
Modern manufacturers achieve security balance through composite construction, combining steel layers with concrete or ceramic materials for enhanced protection without excessive bulk.
Reinforcement Design Features
While steel thickness provides your safe’s primary barrier, reinforcement design features determine how effectively that barrier withstands prolonged attacks. You’ll find that concrete reinforcement notably enhances protection beyond basic steel walls.
TL-15 concrete delivers PSI ratings of 6,300 or higher, making it 162% denser than standard drywall. TL-30 concrete reaches 9,300 PSI, approximately three times stronger than sidewalk concrete.
Composite construction combines multiple materials for ideal security. Steel outer shells resist cutting while concrete cores provide thermal insulation and impact resistance.
Fire-resistant fill materials like gypsum board absorb heat effectively, though they’re less dense than concrete alternatives. Advanced safes integrate ceramic composites or specialized blends to improve resistance without excessive weight.
This layered approach leverages each material’s strengths rather than relying on single-component walls.
Fire and Water Resistance Ratings
Fire ratings serve as your primary guide for determining how long a safe can protect its contents under extreme heat conditions. Standard fire resistance ratings include 30-minute, 1-hour, and 2-hour classifications. A 1-hour rating maintains internal temperatures below 350°F while exposed to 1700°F external heat.
Certification standards like UL 72 and EN 1047-1 require impact testing alongside fire resistance. These tests simulate safes falling through burning floors, ensuring structural integrity remains intact. Internal humidity must stay below 80-85% to prevent moisture damage to electronics and documents.
Water resistance becomes critical during firefighting safety operations. High-volume water can penetrate unsealed safes, destroying contents that survived the fire.
Look for safes featuring waterproof seals and construction designed to withstand both extreme heat and water ingress from suppression efforts. When selecting a safe for your home, consider models with fireproof document bags as an additional layer of protection for your most valuable papers and small items.
Interior Space and Storage Organization
Once you’ve selected a safe with appropriate fire and water protection, interior space becomes your next critical consideration.
Interior dimensions vary dramatically, from compact 0.52 cubic feet models to spacious 20 cubic feet units.
Mid-sized safes typically measure 26″ H x 19.5″ W x 13.5″ D, while larger models reach 56″ height with 23″ width and 12″ depth.
Effective storage solutions maximize your investment.
Look for removable trays approximately 1.5″ deep that separate smaller valuables from larger items.
Adjustable shelving and modular inserts provide customization flexibility.
Premium safes offer tailored interiors with padded compartments protecting delicate jewelry and heirlooms from damage.
Remember that steel thickness reduces usable space compared to external measurements.
Manufacturing tolerances of ±1/8″ affect precise fitting, so measure carefully before purchasing.
Advanced Security Features and Monitoring
Beyond basic locking mechanisms, today’s home safes incorporate sophisticated security technologies that transform simple storage into extensive protection systems. You’ll find biometric access control using fingerprint or facial recognition, eliminating concerns about lost keys or compromised codes. Smart monitoring capabilities connect your safe to smartphones, providing real time alerts for unauthorized access attempts or tampering.
| Security Feature | Technology Type | Alert Capability |
|---|---|---|
| Biometric Access | Fingerprint/Facial Recognition | Immediate notifications |
| Motion Detection | Radar/Laser sensors | Real-time monitoring alerts |
| Video Surveillance | HD cameras with night vision | Remote streaming access |
| Smart Integration | Wi-Fi connectivity | Centralized control system |
Advanced models integrate multiple security layers. Motion sensors detect movement before physical contact occurs. High-definition cameras capture incidents with night vision capabilities. These systems send instant notifications to monitoring services and your mobile devices, ensuring rapid response to security breaches. Many safes also feature water protection ratings that guard against environmental damage from flooding or pipe leaks, providing comprehensive security for both unauthorized access and natural disasters.
User-Friendly Access and Operation
While robust security remains paramount, modern home safes prioritize user convenience through intuitive access methods that eliminate traditional barriers to quick entry.
Biometric security systems enable fingerprint or facial recognition access in under two seconds, removing dependency on memorized codes. Digital keypads support multiple unique PINs for different family members, while smartphone apps provide remote locking capabilities from any location.
Voice assistant integration allows hands-free operation through Alexa or Google Assistant commands.
You’ll appreciate thorough user permissions that let you assign temporary access codes for service providers or houseguests. Clear LCD displays provide immediate feedback, while backlit keypads guarantee accurate entry in low-light conditions.
Physical override keys ensure emergency access during electronic failures, maintaining reliability when you need it most.
Mounting and Installation Considerations
Proper mounting transforms your home safe from a portable container into a permanent security fixture that thieves can’t simply carry away.
Your mounting strategy depends on safe type and available surfaces. Floor safes work best on concrete or solid wood floors, while wall safes require masonry walls or reinforced drywall. Installation precision starts with accurate measurements and proper tool selection.
Essential tools include power drills, levels, and surface-specific hardware like concrete anchors or lag bolts. Pre-drill pilot holes exactly to avoid damaging your safe’s integrity.
Position safes in concealed, low-traffic areas away from electrical wiring. Test stability after installation by attempting slight movements. Heavy-duty expansion bolts should penetrate solid material deeply for maximum resistance.
Follow manufacturer specifications closely to preserve warranty coverage and security features.
Power Management and Backup Systems
When you’re selecting a home safe with electronic locks, you’ll need to understand how power management affects your access during emergencies.
Your safe’s battery life directly impacts security reliability, while emergency override options guarantee you can still open it when the primary power source fails.
Most electronic safes include power failure protection features that maintain lock function and preserve your entry codes even during extended outages.
Battery Life Considerations
Battery performance directly impacts your safe’s reliability, with modern smart safes offering power solutions ranging from basic alkaline systems lasting 12 months to advanced lithium configurations that can operate for up to 8 years.
Effective battery lifespan management requires understanding your usage patterns—frequent access reduces overall battery duration considerably.
Advanced safes feature daily automatic diagnostics that monitor battery health even during inactive periods. These battery health alerts differentiate between batteries requiring immediate replacement versus those with remaining service life.
Digital meters display precise voltage measurements and percentage indicators for accurate monitoring.
Manufacturers recommend annual battery replacement regardless of remaining charge to prevent leakage damage.
Lithium batteries offer superior longevity due to higher energy density and reduced self-discharge rates.
Power-saving technologies like picoPower CPUs and power boost systems maintain consistent performance even when batteries approach depletion.
Emergency Override Options
Even the most reliable battery systems can fail unexpectedly, making emergency override options your final line of defense against complete lockout scenarios.
Physical override keys bypass electronic systems entirely, operating independently of battery power or electrical components. These mechanical keys typically hide behind removable panels or protective covers that prevent tampering while maintaining accessibility during emergencies.
Override key placement varies by manufacturer, but most safes position the keyhole near the main lock mechanism. You’ll need to remove screws or covers to access the manual override.
Emergency access protocols require proper key insertion and turning techniques to avoid damaging the lock mechanism.
Store your override key separately from electronic access codes, ensuring authorized users can locate it quickly during power outages or electronic malfunctions.
Power Failure Protection
Modern home safes rely heavily on electronic systems that become vulnerable during power outages, making robust backup power solutions essential for maintaining security and accessibility.
| Power Solution | Duration | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Backup Batteries | 6-8 hours | Built-in protection, automatic activation |
| UPS Systems | 15-30 minutes | Instant switching, surge protection |
| Portable Generators | Indefinite | Extended runtime with proper fuel |
| Solar Backup | 8-12 hours | Sustainable, silent operation |
| Automatic Generators | Indefinite | Seamless shift, whole-house coverage |
You’ll need extensive surge protection through two-tier systems: whole-house protectors at electrical entry points plus point-of-use devices. AFCI breakers reduce fire risks while GFCI outlets prevent ground faults. Power reliability depends on proper battery maintenance—batteries recharge within 24-48 hours after outages. Managing non-essential functions extends backup duration considerably.
Certification Standards and Testing Requirements
When selecting a home safe that doubles as a storm shelter, you’ll need to verify it meets rigorous certification standards that can mean the difference between life and death during extreme weather events.
FEMA’s P-361 and P-320 guidelines establish the gold standard, requiring resistance against EF-5 tornado winds exceeding 250 mph. ICC 500 certification guarantees structural integrity through thorough testing procedures that simulate high-velocity debris impacts and extreme pressure differentials.
Third-party laboratories conduct these certification tests, evaluating wind resistance and impact protection under controlled conditions. NSSA certification confirms adherence to ICC 500 standards.
The certification benefits include verified performance data, insurance compliance, and legal protection requirements. IBC compliance integrates these standards into local building codes, verifying your safe meets structural safety requirements for both security and storm protection applications.
Warranty Coverage and Long-Term Value
Although certification standards validate your safe’s protective capabilities, warranty coverage determines the long-term financial protection of your investment. Different warranty types range from basic one-year coverage to extensive plans extending ten to twenty years.
Premium manufacturers offer replacement guarantees covering fire damage, theft, and mechanical failures. Cost effectiveness depends on coverage scope versus annual premiums. Basic warranties typically cost $50-150 annually, while extensive plans range $200-500.
Premium manufacturers provide comprehensive replacement guarantees, but cost-effectiveness hinges on balancing coverage scope against annual premium expenses ranging from $50 to $500.
Calculate potential replacement costs against warranty expenses. A $3,000 safe with $200 annual coverage pays for itself if one major incident occurs within fifteen years.
Examine coverage exclusions carefully. Some warranties exclude water damage or require specific installation methods. Transferable warranties add resale value, making your safe more attractive to future buyers when relocating.
Budget-conscious buyers can find reliable options with fireproof and waterproof protection that provide excellent long-term value without compromising essential security features.
On a final note
When selecting your home safe, you’ll need to balance multiple technical specifications against your specific security requirements. The locking mechanism, construction materials, fire ratings, and interior capacity must align with your valuables’ protection needs. Don’t overlook certification standards like UL ratings, which validate performance claims. Consider mounting options, power backup systems, and warranty coverage as indicators of long-term reliability. Your investment should reflect the value you’re protecting inside.