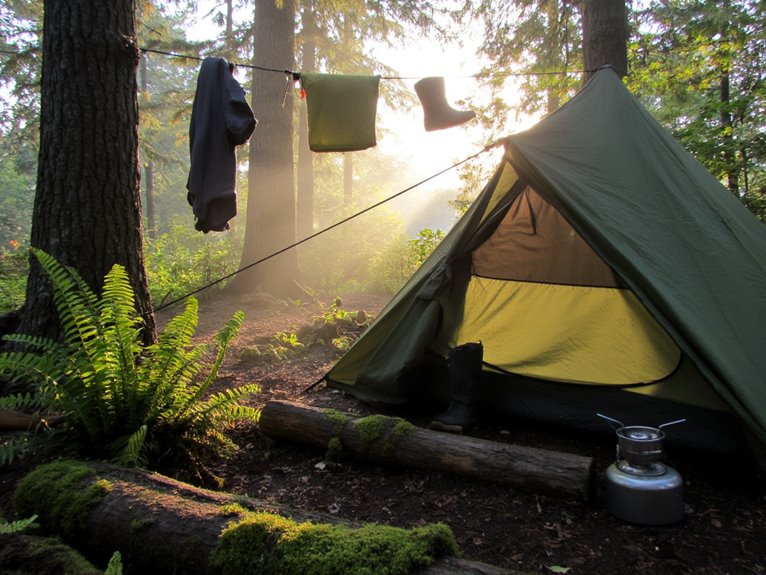
Camping in Humid Climates: Mold Prevention, Breathability, and Drying Gear
When camping in humid climates exceeding 70% humidity, you’ll need active moisture control to prevent mold growth and equipment degradation. Use dehumidifiers, roof vent fans, and mesh windows for continuous airflow while storing gear in breathable containers with silica gel packets. Choose quick-drying synthetic materials like nylon and polyester over cotton fabrics. Position intake vents high and exhaust vents low to maximize air circulation. Digital humidity sensors provide real-time monitoring at breathing level for ideal moisture management throughout your adventure.
We are supported by our audience. When you purchase through links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission, at no extra cost for you. Learn more. Last update on 14th December 2025 / Images from Amazon Product Advertising API.
Notable Insights
- Use dehumidifiers and moisture absorbers in tents and RVs to prevent condensation buildup that leads to mold growth.
- Choose quick-drying synthetic materials like nylon and polyester with DWR-treated sleeping bags for improved moisture resistance.
- Install roof vent fans and multiple low-level exhaust vents to create continuous airflow and prevent stagnant moisture pockets.
- Establish clotheslines between trees and position gear on sunlit surfaces for optimal solar drying after rain exposure.
- Store gear in breathable mesh bags with reusable silica gel packets to absorb residual dampness and prevent mold.
Understanding Humidity’s Impact on Camping Equipment
When you’re camping in humid environments, moisture becomes your gear’s silent adversary, attacking materials through multiple mechanisms that can permanently compromise performance. High humidity above 70% accelerates material degradation by promoting mold and mildew growth on fabric surfaces.
This biological contamination causes discoloration, brittleness, and structural weakening of tents, sleeping bags, and backpacks.
Metal components face accelerated corrosion and rust formation in persistent dampness. Cooking gear and tools lose functionality and safety integrity as oxidation compromises their structural properties. Effective moisture control typically requires maintaining conditions within a temperature range of 40°F-100°F to prevent equipment degradation.
Synthetic and natural fibers absorb moisture directly, weakening durability over time. Fleece-lined materials used in base layers can lose their insulation properties when exposed to excessive moisture during humid camping conditions. Beyond material damage, mold exposure creates health risks that can trigger allergic reactions and respiratory issues for campers.
Humidity also affects sensor accuracy in monitoring equipment. Relative humidity exceeding 75% causes condensation on sensor components, distorting electrical signals and creating measurement hysteresis that overestimates particulate matter readings. Air quality monitors without drying features fail to provide accurate environmental assessments in these conditions.
Essential Moisture Control Strategies for Tents and RVs
You’ll need active moisture removal systems to combat humidity’s relentless assault on your tent or RV’s interior environment.
Dehumidifiers and moisture absorbers work as your first line of defense, pulling excess water vapor from enclosed spaces before condensation forms on surfaces.
Strategic airflow and ventilation systems then create the continuous air exchange necessary to prevent humid air from stagnating and reaching saturation levels inside your shelter. Quality tents feature mesh windows and roofing designed specifically to reduce condensation buildup while maintaining weather protection.
For valuable gear and documents that must stay completely dry, consider storing them in sealed containers with electronic keypads that provide secure, moisture-resistant protection similar to what’s used in high-quality safes.
Dehumidifiers and Moisture Absorbers
Three distinct categories of dehumidifiers and moisture absorbers can transform your humid camping experience from a miserable ordeal into comfortable living.
Refrigerant dehumidifiers excel at removing large moisture volumes quickly with minimal energy consumption, making them cost-effective for RV applications.
Desiccant dehumidifier types maintain consistent performance across all temperatures, including cold climates where refrigerant models fail. These units consume more power but operate quietly.
Non-electric moisture absorption solutions like DampRid work passively without power requirements, ideal when shore power isn’t available.
Small RV dehumidifiers extract one-eighth to one-quarter cup water overnight, markedly reducing condensation and mold risks.
Run units selectively—four hours daily in RVs, eight in tents—to optimize moisture control without causing excessive dryness or discomfort.
Airflow and Ventilation Systems
Proper airflow management serves as your primary defense against moisture accumulation in humid camping environments, where inadequate ventilation can transform enclosed spaces into breeding grounds for mold and condensation.
Different vent fan types address specific moisture control needs. Roof vent fans like the Furrion model offer adjustable speeds for varying humidity conditions, while exhaust fans near kitchens and bathrooms expel moisture-laden air directly. You’ll maximize effectiveness by closing bathroom doors during showers to channel humid air toward vents.
Ventilation mats create moisture barriers under mattresses, maintaining airflow channels even under compression. The rigid loop design of products like Genuine Hypervent prevents dampness where condensation typically forms. Elevated sleeping surfaces with 15+ inch clearance improve air circulation underneath while reducing contact with ground moisture.
Supplement mechanical ventilation by cracking windows slightly and leaving storage spaces partially open to promote continuous air exchange. When sleeping on the ground, choose gear with waterproof materials that resist moisture penetration while allowing trapped air to escape through built-in valve systems.
Maximizing Airflow and Ventilation in Enclosed Spaces
You can’t rely on natural breezes alone when camping in humid conditions—strategic vent positioning creates the pressure differences needed for continuous air exchange in your tent or RV.
Position intake vents on one side and exhaust openings on the opposite side to establish cross-ventilation that maintains air velocities between 0.5-1.2 m/s for effective moisture removal.
Fan circulation techniques amplify this airflow by using portable 12V fans to push stale air out while drawing fresh air in, preventing the pressure equalization that stops air movement.
Strategic Vent Positioning
During humid camping conditions, strategic vent positioning becomes the critical factor that determines whether your shelter maintains comfortable airflow or transforms into a moisture trap.
Proper ventilation strategies require understanding natural air movement patterns to maximize effectiveness. Position your intake vents at the tent’s highest points to capture fresh air, while placing exhaust vents near ground level where heavier moisture accumulates. This top-to-bottom configuration exploits density differences for ideal airflow optimization.
Essential positioning techniques include:
- Supply vents facing prevailing winds to maximize air capture
- Exhaust vents opposite intake points creating continuous airflow loops
- Multiple low-level exits preventing stagnant moisture pockets
- Angled vent orientations directing airflow toward occupied zones
Configure cross-ventilation by aligning openings to channel natural air currents through your shelter, ensuring complete air exchange. Look for tents featuring dual-layer doors that enhance ventilation while providing protection from bugs, maximizing airflow efficiency in humid conditions.
Fan Circulation Techniques
When natural ventilation fails to combat humidity’s relentless assault on your camping shelter, mechanical fan circulation becomes your primary defense against moisture buildup and stagnant air conditions.
Position portable fans to create cross-ventilation patterns that maximize fan efficiency through strategic inlet and outlet positioning. You’ll achieve peak airflow dynamics by placing intake fans low and exhaust fans high, leveraging natural thermal convection principles.
Combine multiple fans in parallel configuration to increase coverage area across larger tents or shelters. Series placement boosts airflow through confined spaces with restrictive openings.
Target air movement over sleeping areas and gear storage zones where moisture accumulates most rapidly. Continuous operation prevents humidity pockets that encourage mold growth.
Select humidity-resistant motors rated for extended outdoor use, ensuring reliable performance throughout multi-day camping expeditions in challenging moisture conditions.
Battery-powered fans provide ventilation solutions without compromising the fuel type requirements of your other essential camping equipment like portable grills and cooking systems.
Proper Techniques for Drying and Storing Camping Gear
Although humid climates present significant challenges for keeping camping gear dry, mastering proper drying and storage techniques will prevent equipment damage and guarantee your comfort throughout the trip.
Begin with squeezing techniques to expel excess water from wet clothing before air drying. Towel drying absorbs significant moisture when you wrap wet items for 20-30 minutes.
Implement these strategic drying methods:
- Establish clotheslines between trees using rope to maximize airflow exposure
- Position gear on sunlit surfaces like tent flies or rocks for solar heat advantage
- Maintain safe distances from heat sources to prevent synthetic fabric damage
- Store damp items in breathable sacks rather than airtight containers
Select quick-drying synthetic materials like nylon and polyester. Use moisture-wicking fabrics and DWR-treated sleeping bags for peak performance. Look for gear featuring ripstop nylon fabric with moisture-wicking technology that provides enhanced durability and quick-dry capabilities essential for humid environments.
Consider investing in spring suspension systems for any portable equipment that requires shock absorption, as these components can significantly improve gear longevity in challenging outdoor conditions.
Monitoring and Managing Humidity Levels During Your Trip
How effectively can you maintain comfortable conditions inside your shelter when humidity levels fluctuate throughout your camping trip? Digital humidity sensors provide real-time moisture level data essential for preventing condensation buildup. Position these instruments at breathing level near sleeping areas and gear storage zones for accurate readings.
| Control Method | Power Requirements | Effectiveness Duration | Maintenance Needs | Coverage Area |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Digital Dehumidifier | Vehicle/Battery Power | 8-12 hours continuous | Empty water tank | 100-200 sq ft |
| Desiccant Packs | None | 24-48 hours | Replace/regenerate | 50-75 sq ft |
| Cross-Ventilation | None | Weather dependent | Position adjustment | Variable |
| Humidity Controller | AC/DC Power | Continuous | Filter cleaning | 150-300 sq ft |
| Silica Gel Canisters | None | 72+ hours | Heating regeneration | 25-50 sq ft |
Combine passive desiccants with active ventilation for ideal moisture control throughout varying weather conditions. When evaluating moisture control equipment, consider factors like durability and fog-resistant performance similar to what you’d find in quality optics. Just as adjustable retention is crucial for securing firearms in quality holsters, proper moisture control requires customizable solutions that can be adjusted based on your specific camping environment and weather conditions.
Long-Term Maintenance and Mold Prevention for Storage
Once your humid climate camping trip ends, the real work begins with proper gear maintenance that’ll determine whether your equipment lasts for years or develops costly mold damage within weeks.
Proper storage tips guarantee maximum gear longevity through systematic preparation:
Systematic preparation and proper storage techniques are the foundation for maximizing your camping gear’s lifespan and performance.
- Complete drying: All tents, sleeping bags, and tarps must reach zero moisture content before storage.
- Climate-controlled environment: Store in areas with consistent 30-50% humidity and 60-75°F temperatures.
- Breathable containers: Use mesh bags or old pillowcases instead of compression sacks for fabric items.
- Moisture absorption: Place reusable silica gel packets with stored equipment to eliminate residual dampness.
Clean all gear with mild, non-detergent soaps immediately after use. Remove organic matter that promotes mold growth.
Store items elevated on shelves with adequate airflow spacing. Inspect equipment monthly for early mold detection and material degradation signs.
Rain jackets with compression storage features can be particularly valuable additions to your humid climate camping gear setup, allowing for efficient packing while maintaining protective capabilities.
The same moisture-wicking technology principles that make outdoor clothing effective also apply to base layer garments and undergarments, helping maintain dryness during extended camping activities in humid environments.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I Use Regular Household Dehumidifiers in Camping Situations Without Electrical Hookups?
No, you can’t use regular household dehumidifiers without electrical hookups. Instead, consider dehumidifier alternatives like calcium chloride crystals or silica gel packs, plus improve camping ventilation through proper airflow and tent positioning.
What’s the Difference Between Moisture-Wicking Storage Bags and Regular Plastic Bags?
Moisture-wicking bags allow air circulation and moisture absorption, preventing mold while plastic bags trap humidity. They’re better for temperature regulation and drying gear, though you’ll pay more upfront for durability.
How Often Should I Replace Moisture-Absorbing Crystals or Chemical Packets Like Damprid?
You should replace moisture-absorbing crystals every 30-45 days under normal conditions, but in humid climates every 2-4 weeks. Monitor moisture crystal longevity closely and adjust humidity control techniques based on environmental conditions.
Are There Specific Tent Fabrics That Resist Mold Better Than Others?
Yes, silicone-coated fabrics offer unmatched mold resistance due to their hydrophobic properties, while PE-coated tent materials also provide extremely high resistance. Dyneema laminates don’t absorb moisture, naturally discouraging mold formation.
On a final note
You’ve now got the essential knowledge to combat humidity’s challenges during camping trips. Implement proper ventilation techniques, maintain airflow rates above 4 CFM per person, and monitor relative humidity below 60%. Your gear’s longevity depends on consistent drying protocols and strategic moisture management. Don’t let condensation and mold ruin your equipment investments. Apply these technical strategies systematically, and you’ll preserve your camping gear while enjoying comfortable, dry outdoor experiences regardless of climate conditions.