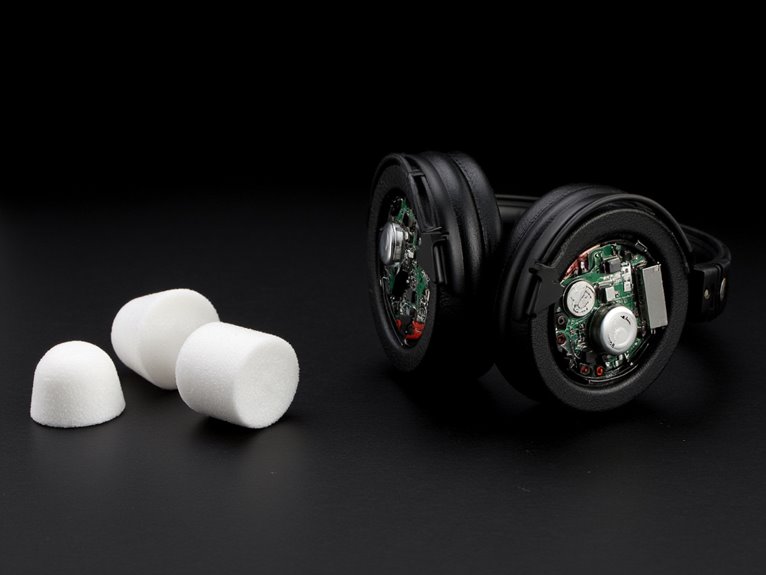
Passive Vs Electronic Hearing Protection: Differences and Benefits
Passive hearing protection creates acoustic seals using sound-absorbing materials and physical barriers, achieving 25-31 dB NRR without requiring power or batteries. Electronic models combine passive blocking with active noise cancellation circuits that detect ambient noise through microphones and counter sound waves with phase-inverted signals. While passive devices offer consistent, uniform protection at lower costs ($13-30), electronic versions provide selective filtering, environmental awareness, and communication capabilities but require ongoing battery expenses and higher initial investment ($39-800+). Understanding these fundamental differences helps you choose the best protection for your specific noise environment and operational requirements.
We are supported by our audience. When you purchase through links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission, at no extra cost for you. Learn more. Last update on 27th December 2025 / Images from Amazon Product Advertising API.
Notable Insights
- Passive hearing protection uses sound-absorbing materials to block noise, while electronic models actively cancel sound using microphones and phase-inverted waves.
- Electronic devices provide selective noise reduction and environmental awareness, allowing communication while maintaining protection in dynamic environments.
- Passive earmuffs cost $13-30 with no ongoing expenses, while electronic models range $39-800+ and require continuous battery replacements.
- Electronic protection excels in shooting sports and tactical environments, while passive works best for consistent noise like manufacturing or concerts.
- Passive models are lighter and more durable with simpler mechanisms, while electronic versions offer adaptive technology but are heavier and more fragile.
How Passive and Electronic Hearing Protection Work
When choosing between passive and electronic hearing protection, understanding their fundamental operating principles will guide you toward the right solution for your specific noise environment.
Passive mechanisms operate through physical barriers that create acoustic seals around your ears. These devices use sound-absorbing materials inside earmuff cups or earplug bodies to block sound waves from reaching your eardrum. They don’t require power and reduce all noise levels uniformly. Circumaural earmuffs create an effective seal over the entire ear using sound-absorbing fill material.
Passive hearing protection creates physical barriers using sound-absorbing materials to uniformly block all noise without requiring power sources.
Electronic circuitry takes a different approach by actively processing sound. Built-in microphones capture ambient noise while speakers deliver filtered audio to your ears. The system performs active noise cancellation by generating phase-inverted sound waves that counteract incoming noise. This allows amplification of quiet sounds like speech while suppressing harmful loud noises, requiring battery power for operation. Electronic hearing protection devices combine electronic and structural components to provide this dual functionality.
Noise Reduction Performance Comparison
The numbers tell a clear story about which protection method delivers excellent noise reduction for your specific needs. Passive earmuffs typically achieve 25-31 dB NRR through physical sound barriers.
Electronic devices match or exceed these performance metrics through adaptive technology.
Real-world testing reveals significant differences. At 100 dBA noise levels, earplugs create masked thresholds around 91.9 dBA. Active noise reduction earmuffs perform better at approximately 93.8 dBA, while passive earmuffs show slightly reduced effectiveness at 95.5 dBA.
Electronic protection’s advantage lies in selective noise reduction. You’ll experience dynamic suppression of harmful peaks while preserving environmental awareness.
Passive devices reduce all frequencies equally, limiting your ability to distinguish essential sounds. Proper fitting remains vital for both types, though electronic models offer better sound differentiation when sealing is ideal.
For lawn mowing applications, models like the GUCHO Safety Muffs provide 34dB noise reduction through passive construction, making them highly effective for protecting against the harmful noise levels generated by mowers.
Advanced electronic hearing protection features adjustable settings that allow users to customize protection levels for different shooting environments while maintaining enhanced hearing for important sounds.
Best Applications for Each Protection Type
Five distinct environments determine which hearing protection type delivers ideal performance for your specific situation.
Electronic models excel in shooting sports, construction sites, and tactical environments where communication remains critical. You’ll benefit from automatic shut-off features and Bluetooth connectivity during competitive shooting or machinery operations. These devices amplify safe ambient sounds while blocking harmful impulse noise above 82 dB.
Passive protection suits motor sports, concerts, and manufacturing settings with constant noise exposure. You won’t need batteries or electronic components during extended sessions.
Selection criteria include noise consistency, communication requirements, and power availability. Electronic protection costs more upfront but enhances safety through preserved situational awareness. Passive devices offer superior reliability and lighter weight for prolonged wear.
Best applications depend on balancing cost, durability, and operational communication needs.
Comfort and User Experience Factors
Comfort determines how long you’ll actually wear hearing protection, making user experience factors critical for effective noise control. Electronic models offer adjustable features that let you customize your experience based on environmental demands and wearer preferences.
Key comfort differences include:
- Weight distribution – Passive earmuffs weigh less due to simpler construction, while electronic models carry additional hardware burden.
- Pressure consistency – Thick cushioning in passive models provides uniform pressure but may feel bulky during extended wear.
- Ambient awareness – Electronic protection maintains situational awareness through selective sound filtering, reducing sensory isolation.
- Environmental adaptability – Adjustable volume controls in electronic devices prevent unnecessary isolation in changing noise conditions.
Electronic hearing protection’s adaptive sound control technology enhances communication without compromising safety, making it superior for dynamic environments requiring sustained wear. Modern electronic earbuds designed for shooting offer situational awareness features with impressive battery life ranging from 10 to 25 hours for extended shooting sessions.
Cost Analysis and Long-Term Value
While initial purchase price often drives hearing protection decisions, total ownership costs reveal a more complex financial picture that extends far beyond the checkout counter.
Passive models deliver superior cost effectiveness, ranging from $13 to $30 with zero ongoing expenses. You’ll get NRR ratings of 24-30 dB without battery replacements or maintenance costs.
Electronic protection starts at $39 but can exceed $800 for premium models. You’ll face continuous battery expenses—though quality units provide 220 hours per zinc-air set.
Investment longevity favors passive designs due to robust construction and simpler mechanisms.
Electronic models offer enhanced features like selective amplification and communication capabilities, but they’re more vulnerable to moisture damage and component failure, potentially requiring more frequent replacements despite warranty coverage.
Frequently Asked Questions
Do Electronic Hearing Protectors Work Properly in Extreme Weather Conditions Like Rain?
Yes, electronic hearing protectors work in rain with IPX4+ water resistance ratings and nano-coatings. However, you’ll experience reduced performance in extreme cold due to temperature effects on batteries and electronics. σε
On a final note
You’ll need to match your hearing protection to your specific environment and budget. Passive protection delivers consistent, reliable noise reduction at lower costs for steady-noise environments. Electronic protection offers superior versatility with situational awareness capabilities, making it ideal for dynamic settings despite higher initial investment. Consider your primary use case, required NRR levels, and long-term durability needs when making your selection decision.