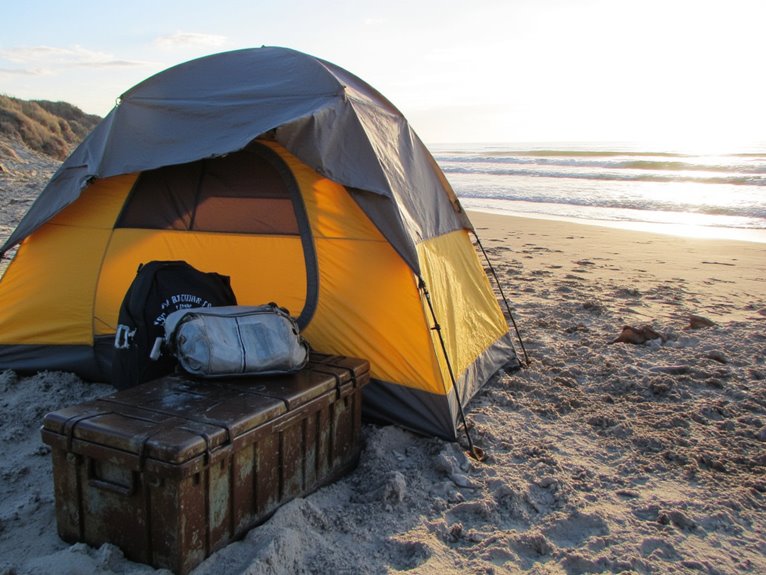
Coastal & Beach Camping: Tides, Corrosion, and Sandproofing Gear
Successful coastal camping requires mastering three critical challenges: understanding tidal patterns, preventing saltwater corrosion, and sandproofing your gear. You’ll need tide charts to avoid flooding, as high tides can reach 50 feet above low tide marks. Rinse all metal equipment with fresh water for five minutes after beach exposure, and use marine-grade anti-corrosion coatings with 95% zinc dust. Select tightly woven ripstop nylon fabrics and sand-specific stakes for effective sand resistance. Thorough preparation techniques will maximize your coastal camping success.
We are supported by our audience. When you purchase through links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission, at no extra cost for you. Learn more. Last update on 18th January 2026 / Images from Amazon Product Advertising API.
Notable Insights
- Use tide charts and apps to predict daily high/low tides, marking high-tide lines with rocks during low tide for safe campsite selection.
- Rinse all metal gear with fresh water for five minutes after beach use and apply marine-grade anti-corrosion coatings for protection.
- Choose tightly woven synthetic fabrics like ripstop nylon and sealed storage containers to prevent persistent sand infiltration into gear.
- Secure tents with sand anchors rated for 40+ mph winds and use sand pockets instead of traditional stakes for better anchoring.
- Position campsites upwind from prevailing winds and use tarps at tent entrances as effective sand barriers for gear protection.
Understanding Tidal Patterns for Safe Campsite Selection
When planning coastal beach camping, understanding tidal patterns isn’t just helpful-it’s essential for your safety and the success of your trip. Tidal cycle importance becomes clear when you consider that some locations experience high tide lines up to 50 feet above low tide marks.
Each 24-hour period brings two high tides and two low tides, with heights and timing shifting daily.
Effective tide prediction methods include using tide charts, mobile apps, and traditional printed tables. Download offline data before departure since cell service may be unavailable.
Look for visual indicators like darker wet sand, debris lines, and log jams that mark previous high-tide reaches. These natural markers help you identify safe camping zones above the flood line, preventing overnight tent inundation. During low tide, mark the high-tide line with rocks or driftwood to maintain a clear visual reference as water levels change throughout your stay. Always ensure your campsite is at least 100 feet from the waterline to provide adequate safety margin during high tide cycles.
Protecting Metal Gear From Saltwater Corrosion
Saltwater creates one of the most aggressive corrosive environments your camping gear will ever face. Salt spray accelerates oxidation rates exponentially compared to freshwater exposure. Implement preventive measures immediately after each beach session by rinsing all metal components with fresh water for a minimum of five minutes.
Apply marine-grade anti-corrosion coatings containing 95% zinc dust for sacrificial protection. Choose 316 stainless steel hardware over standard metals. Type 316 offers superior chloride resistance compared to 304 stainless steel.
Install physical barriers like waterproof casings and wind shields to limit direct salt contact. Store gear with desiccants in controlled environments when possible. Establish corrosion monitoring protocols through regular visual inspections.
Check for white residue buildup, pitting, or discoloration patterns. Replace sacrificial anodes before complete consumption occurs to maintain continuous electrochemical protection.
Essential Sandproofing Techniques and Equipment
Sand infiltration poses one of the most persistent challenges you’ll face during coastal camping, requiring strategic gear selection and campsite management to maintain comfort and equipment functionality.
Your choice of sand-resistant materials and protective equipment directly impacts your camping experience, with tightly woven synthetic fabrics like ripstop nylon proving 40-60% more effective at blocking fine particles than loose-weave cotton alternatives.
Proper campsite positioning combined with barrier systems can reduce sand contamination by up to 80% when you implement upwind placement and establish designated sand zones at tent entry points.
For sensitive electronics and metal equipment exposed to coastal conditions, consider incorporating desiccant canisters or moisture-absorbing solutions that require no electrical power and can protect gear in spaces up to 60 cubic feet from salt air and humidity damage.
Sand-Resistant Gear Selection
Beyond the obvious challenge of keeping your sleeping bag comfortable, selecting sand-resistant gear requires understanding how different materials and designs interact with coastal environments.
Sand resistant mats featuring dual-layer high-density polyethylene mesh allow sand to sift through while trapping debris on top. These mats range from 6×6 ft to 12×12 ft, accommodating various camping setups. Non-absorbent materials prevent liquid stains and enable easy cleaning.
Choose tents with bathtub-style floors and raised edges to block sand intrusion. Fewer, larger zippers minimize sand catch points that cause failures.
Synthetic fabrics made from recycled plastic-based textiles resist sand adhesion better than natural materials. Sealed storage containers with smooth surfaces prevent sand embedding in your gear during transport.
For head protection in sandy conditions, consider headwear with satin lining that reduces friction and prevents sand particles from catching in hair while maintaining comfort during windy coastal camping.
When selecting outerwear for coastal camping, prioritize jackets with adjustable features that can seal against blowing sand while maintaining breathability during beach activities.
Campsite Setup Strategies
When establishing your coastal campsite, proper location selection forms the foundation of effective sand management throughout your stay. Position your shelter where vegetation meets sand to gain natural wind protection while maintaining firmer ground for staking.
Avoid areas below high-tide markers indicated by seaweed lines and driftwood deposits.
Create designated sand barrier zones using tarps at tent entrances. Place outdoor mats both inside and outside your shelter to intercept sand particles before they penetrate living spaces. Strategic tent orientation away from prevailing winds reduces sand accumulation considerably.
Deploy sand-specific stakes rated for coastal conditions to secure your setup against oceanic breezes. Maintain water buckets and towels at entry points for foot rinsing protocols.
Regular campsite maintenance includes sweeping shelter floors and shaking out bedding to prevent sand buildup throughout your stay. Consider using waterproof closed-cell foam padding beneath your sleeping area to create an additional moisture barrier while providing extra comfort against the sandy ground.
Beach-Adapted Shelter and Sleeping Solutions
Because coastal environments present unique challenges that standard camping gear can’t handle, selecting the right shelter and sleeping equipment becomes critical for successful beach camping. Beach shelter innovations focus on UV-resistant fabrics with UPF 50+ ratings and reinforced composite fiber poles that flex with coastal winds. Sand pockets replace traditional stakes for secure anchoring.
| Feature | Shelter Solution | Sleeping Solution | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wind Resistance | Flexible composite poles + sand anchors | Elevated cots/pads | Stability in gusts |
| Sand Protection | Easy-clean polyester surfaces | Closed-cell mattress coating | Repels particles |
| Corrosion Control | Aluminum/fiberglass frames | Ripstop nylon sleeping bags | Salt-air durability |
| Ventilation | Mesh windows + roll-up panels | Moisture-wicking linings | Humidity management |
Sand resistant sleeping gear utilizes closed-cell surfaces and breathable materials that don’t retain moisture or particles.
Coastal Cooking and Food Storage Strategies
Food preservation and cooking at coastal campsites demands specialized strategies that account for salt air, humidity, and limited refrigeration options.
High-quality rotomolded coolers maintain ice for up to five days, functioning as portable freezers. Pre-frozen meats and ice packs optimize temperature control for effective meal prep.
Bear-resistant containers and scent-proof bags protect food storage from coastal wildlife. Hang food bags 10 feet high and 4 feet from tree trunks, or use hard-sided bear canisters for maximum security.
Metal food lockers provide communal storage in developed campgrounds.
Airtight plastic containers prevent moisture contamination and organize provisions efficiently. Portable camp stoves handle windy beach conditions better than open flames. Wind-resistant designs with stabilizing features ensure consistent cooking performance despite fluctuating coastal conditions that can disrupt heat output and flame control.
Plan one-pot meals requiring minimal refrigeration when ice resupply isn’t available.
Safety Equipment and Comfort Essentials for Beach Environments
Why do coastal camping adventures turn dangerous so quickly without proper safety equipment? Beach environments present unique hazards requiring specialized gear. Your first aid essentials must include waterproof bandages, antiseptic wipes, and antibiotic ointment for treating cuts from shells or coral.
Pack instant cold packs and hydrocortisone cream for jellyfish stings and allergic reactions.
Emergency equipment should feature a loud whistle for signaling rescue teams across windy beaches. Include fire extinguishers rated for cooking equipment and emergency contact cards in waterproof cases.
UV protection requires SPF 30+ sunscreen, polarized sunglasses, and wide-brimmed hats.
Choose corrosion-resistant camping chairs with aluminum frames and synthetic fabrics. Store electronics in IP67-rated waterproof cases.
Secure tents using sand anchors rated for 40+ mph winds to prevent equipment loss during coastal storms. For wildlife observation during your coastal camping experience, invest in waterproof binoculars with rubber-armored construction like the Celestron Nature DX series to withstand salt spray and beach conditions.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Permits or Reservations Are Required for Beach Camping in Different Areas?
Beach camping permits vary by location with different reservation policies. You’ll need Hawaii State permits up to one year ahead, Honolulu permits two weeks prior, or Kaua’i County permits with specific fees.
How Do You Properly Dispose of Waste and Greywater While Beach Camping?
Pack out all trash and food scraps following “pack it in, pack it out” principles. For greywater disposal, strain food particles and dispose at least 200 feet from water sources using biodegradable soap sparingly.
What Are the Best Methods for Securing Campfires on Sandy Beaches?
You’ll need elevated metal fire pit options with solid bottoms instead of digging sand pits. Follow local safety regulations requiring permits, maintain 50-foot clearances from vegetation, and use only approved fuels like charcoal or clean wood.
How Can You Identify and Avoid Protected Wildlife Nesting Areas When Camping?
You’ll spot wildlife nesting areas by looking for orange flagging, roped boundaries, and informational signs. Practice wildlife awareness during nesting season by staying on wet sand below high-tide lines and respecting all posted restrictions.
On a final note
You’ve now got the essential knowledge to tackle coastal camping challenges head-on. Proper tide timing prevents washouts. Quality corrosion protection extends your gear’s lifespan by years. Effective sandproofing keeps equipment functional when it matters most. These techniques aren’t optional-they’re requirements for successful beach camping. Apply these strategies consistently, and you’ll enjoy safe, comfortable coastal adventures while protecting your investment in quality outdoor gear.