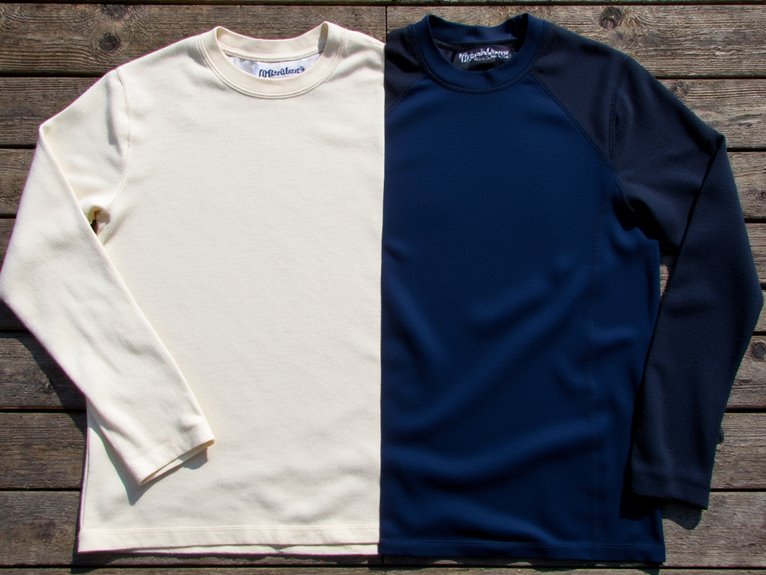
Merino Wool Vs Synthetic Base Layers: Pros, Cons, and Choosing the Best
You’ll find merino wool excels in odor resistance and temperature regulation, retaining up to 30% moisture while feeling dry, making it ideal for multi-day adventures and cold weather activities. Synthetic base layers dry 3-5 times faster and offer superior durability, lasting 2-3 times longer with better tear resistance, perfect for high-intensity activities. Merino costs $60-130 versus synthetics at $45-90, but provides natural antimicrobial properties that synthetics can’t match long-term. Understanding specific performance characteristics will guide your best choice.
We are supported by our audience. When you purchase through links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission, at no extra cost for you. Learn more. Last update on 27th January 2026 / Images from Amazon Product Advertising API.
Notable Insights
- Merino wool excels in warmth retention and odor resistance, while synthetic materials prioritize rapid moisture wicking and faster drying performance.
- Synthetic base layers cost $45-90 and last 2-3 times longer than merino wool options priced at $60-130.
- Merino wool feels softer against skin and maintains comfort when wet, whereas synthetics can feel clingy during moisture exposure.
- Choose synthetics for high-intensity activities requiring breathability; select merino wool for cold weather and multi-day adventures needing odor control.
- Merino wool biodegrades naturally but requires gentle care, while synthetic materials resist tears better but persist indefinitely in landfills.
Understanding Base Layer Materials and Their Properties
When selecting a base layer for outdoor activities, understanding the fundamental differences between merino wool and synthetic materials becomes essential for peak performance.
Merino wool originates from Merino sheep, consisting of protein-based keratin fibers with crimped structures that trap air effectively. These natural fiber sources create superior warmth-to-weight ratios compared to synthetic alternatives.
Merino’s crimped keratin fibers create natural air pockets, delivering exceptional warmth-to-weight performance that synthetic materials struggle to match.
Synthetic base layers derive from petrochemical-derived polymers like polyester and nylon. Their hydrophobic nature enables faster moisture transport and drying times. However, material ethics considerations include environmental impact differences between renewable wool production and petroleum-based manufacturing.
Merino’s semi-hydrophobic structure absorbs moisture internally while repelling surface water. Synthetics resist moisture absorption entirely, maintaining insulation properties through different mechanisms. High-quality polyester can absorb only about 0.4% of its weight in water, making it exceptionally efficient at maintaining dryness.
Both materials offer distinct advantages: merino excels in odor resistance and thermal regulation, while synthetics provide superior durability and abrasion resistance for demanding applications. Mid-weight polyester garments demonstrate exceptional long-term durability, with some users reporting decades of effective performance without significant degradation. For activities involving water exposure, moisture-wicking capabilities become crucial for maintaining comfort and preventing moisture-related problems during extended outdoor adventures.
Moisture Wicking and Drying Performance Comparison
These material properties directly influence how base layers handle moisture during physical activity, with synthetic and merino wool fibers employing fundamentally different approaches to sweat management.
Synthetic fibers excel at rapid moisture transport through their hydrophobic nature and capillary action. You’ll experience quick sweat removal from skin to fabric surface, with drying speed often occurring within minutes after activity stops. This prevents fabric saturation during high-intensity pursuits like running or cycling.
Merino wool uses moisture retention as an advantage, absorbing sweat within fiber layers while maintaining comfort. The natural crimp structure provides gradual evaporation and temperature regulation, though drying speed remains slower than synthetics. When selecting base layers for moderate weather conditions, understanding these drying differences becomes essential for choosing insulation type that matches your activity level and climate requirements.
- Synthetic layers dry 3-5 times faster than merino wool due to minimal water absorption.
- Merino wool retains up to 30% of its weight in moisture while feeling dry.
- Fast-drying synthetics maintain lightweight performance during repeated high-output activities.
Similar to how portable camping grills require optimal BTU output for efficient cooking performance, base layers need proper moisture management systems to maintain comfort during outdoor activities.
Comfort Levels and Temperature Regulation Capabilities
Beyond moisture management, how well base layers regulate temperature and maintain comfort depends largely on the fundamental structural differences between merino wool and synthetic fibers.
Merino wool’s natural crimp creates insulating air pockets that trap body heat efficiently while allowing controlled moisture release. This temperature adaptation keeps your skin comfortable across varying conditions, maintaining warmth even when wet and preventing hypothermia risks in cold environments.
The comfort comparison reveals distinct differences.
Merino’s fine fibers (<24 microns) feel soft against skin, while synthetics often lack this tactile quality. Wool fibers dynamically adjust to environmental changes, providing consistent comfort through their moisture-interactive properties.
Synthetic layers excel during high-intensity activities with rapid air movement and quick-drying capabilities, but they lose insulation when wet and may feel clingy when saturated.
Odor Control and Multi-Day Wear Performance
Although both materials handle moisture effectively, their approach to odor control reveals fundamental differences that dramatically impact multi-day performance.
Merino wool’s intrinsic antimicrobial properties provide superior bacteria growth prevention that won’t wash out over time. You’ll experience consistent odor resistance benefits throughout extended trips without laundering access.
Synthetic fabrics rely on chemical treatments that diminish with repeated washing. While they wick moisture faster, they trap odors more readily due to bacterial buildup on fibers.
Key odor control advantages of merino wool:
- Natural antimicrobial properties that inhibit bacteria growth permanently
- Multi-day wear capability without noticeable smell accumulation
- Moisture absorption while maintaining freshness between washes
For extended outdoor adventures prioritizing odor control, merino wool consistently outperforms synthetics despite slower drying times. High-quality merino wool can endure hundreds of wash cycles while maintaining its natural odor resistance properties, ensuring long-term value for outdoor enthusiasts.
Durability, Care Requirements, and Longevity
When choosing between merino wool and synthetic base layers, you’ll face a clear trade-off between durability and maintenance requirements that directly impacts your long-term investment.
Synthetic fabrics consistently outperform merino wool in resistance to tears, pilling, and abrasion while requiring minimal care-machine washable, quick-drying, and maintaining their shape through hundreds of wash cycles.
Merino wool demands gentle hand washing or wool-specific cycles, careful drying procedures, and more frequent replacement due to its natural fiber vulnerability to physical wear and improper handling.
Fabric Durability Comparison
Synthetic base layers consistently outperform merino wool in durability tests, showing superior resistance to tears, snags, and abrasion under rigorous outdoor conditions.
Durability testing reveals that synthetic fibers maintain structural integrity markedly longer than natural wool fibers. You’ll find synthetic materials resist fiber abrasion from backpack straps and equipment friction that quickly damages delicate merino wool.
- Wear resistance: Synthetic fabrics withstand heavy use without pilling or fiber breakage
- Moisture retention impact: Wool’s water absorption weakens fibers over time, while synthetics stay structurally sound
- Service life: Synthetic base layers typically last 2-3 times longer than pure merino wool options
Synthetic fabrics dry faster, reducing moisture retention that degrades natural fibers.
High-quality synthetics incorporate engineered fibers specifically designed for abrasion resistance and longevity.
Washing and Maintenance
Care requirements reveal substantial differences between merino wool and synthetic base layers that directly impact their long-term performance and value.
You’ll need cold water and gentle cycles for merino wool, while synthetics handle standard machine washing. Avoid fabric softeners and bleach with wool-they damage fibers and reduce odor control.
Synthetic layers dry faster and require less attention. However, merino wool’s natural odor resistance means fewer washes overall.
Key maintenance tips include air-drying wool to prevent shrinkage and using specialized detergents when needed.
Proper washing techniques extend garment lifespan considerably. Synthetics maintain shape through multiple cycles, but merino wool requires careful handling.
You’ll spend more time caring for wool, but it’ll reward you with years of performance when maintained correctly.
Long-Term Value Assessment
Beyond immediate performance considerations, your choice between merino wool and synthetic base layers greatly impacts long-term ownership costs and replacement frequency.
Synthetic base layers demonstrate superior resistance to tears, snags, and abrasion, delivering extended usable lifespans that often exceed merino wool by 30-40%. User testimonials consistently report synthetic layers maintaining structural integrity through 200+ wash cycles, while merino wool shows fiber degradation around 100-150 cycles.
- Durability advantage: Synthetics resist pilling and maintain shape better than merino wool’s susceptible natural fibers
- Care requirements: Merino demands delicate handling and moth protection, while synthetics tolerate aggressive washing
- Performance expectations: Synthetics retain moisture-wicking functionality longer, though merino’s odor resistance initially outperforms
Blended fabrics offer compromise solutions, extending merino’s lifespan while preserving key benefits. When choosing between materials, consider factors such as durability and water resistance for protection in unpredictable weather conditions. Similar to outdoor gear like camping cots, fabric surfaces can be maintained with simple wet cloth cleaning to extend their usable life.
Cost Analysis and Environmental Impact
When you’re choosing between merino wool and synthetic base layers, you’ll face a clear trade-off between higher upfront costs and long-term environmental considerations.
Merino wool base layers typically cost $60-130 compared to synthetic options at $45-90, but this price difference only tells part of the story.
Your decision becomes more complex when you factor in each material’s environmental footprint, durability characteristics, and total cost of ownership over multiple seasons of use.
Initial Purchase Price Comparison
Although synthetic base layers offer immediate savings at checkout, merino wool‘s higher upfront investment tells only part of the cost story. Synthetic options typically range from $40-$90, while merino wool pieces cost $60-$120 depending on weight and brand. Price elasticity shows consumer preferences often favor synthetics for budget-conscious purchases, yet merino’s superior longevity changes the equation.
Key Price Factors:
- Merino wool production involves expensive sheep farming, shearing, and complex processing compared to petroleum-based synthetic manufacturing.
- Synthetic base layers benefit from mass production economies of scale, keeping costs consistently lower.
- Blended materials (80-90% merino with synthetics) offer moderate pricing between pure options.
Heavyweight merino commands premium pricing due to increased material density (measured in g/m²), while synthetics maintain stable pricing across weight categories.
Environmental Footprint Analysis
Environmental impact calculations reveal stark differences between merino wool and synthetic base layers across their complete lifecycles. You’ll find merino wool contributes 47.7% of fossil fuel use during manufacturing, while synthetic fibers require petroleum-based production processes that generate higher initial greenhouse gas emissions.
| Impact Category | Merino Wool | Synthetic Fibers |
|---|---|---|
| Water Pollution | 291x more pollutants than freshwater | Microplastic release during washing |
| End-of-Life | Fully biodegradable | Persists indefinitely |
| Manufacturing Energy | High water/energy for scouring | Energy-intensive petroleum processes |
| Sourcing Options | Regenerative agriculture practices | Recycled variants available |
Ethical sourcing certifications like ZQ Merino promote sustainable farming that reduces land degradation. Synthetic recycled variants appreciably decrease environmental harm by diverting plastic waste from landfills. Similar to how rechargeable designs enhance long-term cost-effectiveness in moisture control products, sustainable base layer choices provide ongoing environmental benefits through extended product lifecycles. When selecting base layers, consider that merino wool typically requires more specific care instructions for washing and drying compared to synthetic options, which can impact both garment longevity and your daily maintenance routine.
Long-Term Value Assessment
Three critical factors determine whether merino wool or synthetic base layers deliver superior long-term value: initial cost versus lifespan, maintenance requirements, and performance benefits that reduce gear needs.
Merino wool’s $60-120 price range exceeds synthetic’s $45-90 cost. However, wool’s odor resistance extends wear cycles, reducing laundry frequency and associated costs.
Synthetic layers offer superior durability and simpler care requirements, translating to better cost-per-wear for high-abrasion activities.
User preferences greatly impact value calculations. User experiences vary based on activity type and care habits.
Similar to how 40D nylon materials in sleeping pads prioritize longevity over cheaper alternatives, investing in quality base layer fabrics often justifies higher upfront costs through extended performance lifespan.
- Multi-season versatility: Wool’s temperature regulation reduces need for multiple base layers
- Maintenance costs: Synthetic’s harsh-wash tolerance versus wool’s gentle care requirements
- Replacement frequency: Synthetic durability versus wool’s odor control extending usable life
Activity-Specific Recommendations and When to Choose Each
Your choice between merino wool and synthetic base layers depends heavily on your specific activity, environmental conditions, and performance priorities.
For high-intensity activities like running and cycling, synthetic fabrics deliver superior moisture-wicking and breathability, preventing overheating during heavy exertion. Their fast-drying properties and durability make them ideal for rugged environments.
Cold weather and multi-day adventures favor merino wool’s natural advantages. It retains warmth when wet and offers exceptional odor resistance for extended wear.
The material suitability becomes clear in backcountry hunting, where wool’s silent fabric properties aid stealth while synthetics excel during stalking phases.
Activity recommendations also consider budget constraints. Synthetics provide affordable, low-maintenance options with varied styling.
Merino wool justifies higher costs through comfort, sustainability, and natural temperature regulation across diverse conditions. For those with high arches, proper footwear selection becomes equally important to prevent discomfort during extended outdoor activities.
For long-distance hiking adventures, both materials benefit from pairing with breathable footwear that manages moisture and heat effectively during extended trail time.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can You Mix Merino Wool and Synthetic Pieces in the Same Layering System?
Yes, you can mix merino wool and synthetic pieces effectively. Blending advantages include enhanced moisture management and odor control. Smart layering strategies involve merino bases for warmth plus synthetic outer layers for faster drying.
Do Merino Wool Base Layers Pill or Develop Holes With Regular Use?
You’ll experience minimal pilling with merino wool base layers compared to synthetics. However, they’re less durable and may develop holes over time with frequent washing and wear, making pilling prevention and durability comparison important considerations.
Can Synthetic Base Layers Cause Skin Irritation or Allergic Reactions?
Yes, synthetic base layers can trigger skin irritation and allergic reactions. If you have skin sensitivity, you might experience allergy symptoms like redness, itching, or rashes from chemical treatments and poor breathability in synthetic fabrics.
On a final note
You’ll find success with either material when you match it to your specific needs. Choose merino wool for multi-day adventures, cold conditions, and odor control priorities. Select synthetic base layers for high-output activities, budget constraints, and quick-drying requirements. Don’t overthink the decision-both materials perform effectively in their intended applications. Consider your activity duration, weather conditions, and personal preferences when making your final choice.