Wind-Proof Campsite Setup: Orientation, Low-Profile Shelters, and Guying
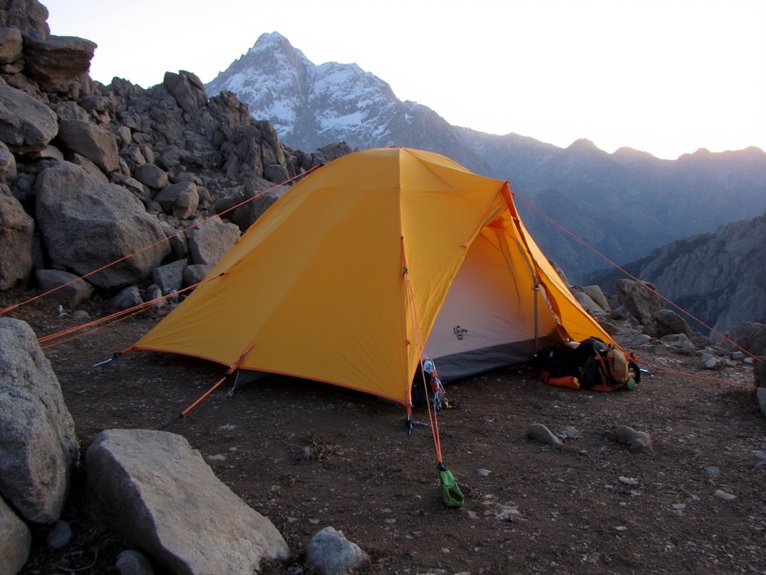
Position your tent’s narrow end directly into prevailing winds to reduce wind pressure by 60% compared to broadside positioning. Angle your shelter 27° to 45° diagonally for best wind load distribution. Choose low-profile designs with gently sloping panels-hexagonal and octagonal shapes offer superior resistance. Implement multi-point guying with stakes at 45-degree angles for maximum ground holding strength. Start staking from the windward side and supplement with natural anchors for enhanced stability in challenging conditions.
We are supported by our audience. When you purchase through links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission, at no extra cost for you. Learn more. Last update on 18th January 2026 / Images from Amazon Product Advertising API.
Notable Insights
- Position tent’s narrow end into prevailing winds at 27-45° diagonal angle to reduce wind pressure by up to 60%.
- Choose low-profile shelters with hexagonal, octagonal, or conical designs that allow wind to flow smoothly overhead without resistance.
- Use multi-point guying with stakes angled at 45 degrees, starting from windward side for maximum ground holding strength.
- Select campsites below treeline with natural ground contouring and krumholtz protection while avoiding exposed ridges and wind corridors.
- Balance guy line tension between tautness and flexibility, supplementing stakes with natural anchors to prevent fabric tears during gusts.
Optimal Tent Positioning Against Wind Forces
When setting up camp in windy conditions, your tent’s orientation becomes the critical factor determining whether you’ll sleep comfortably or spend the night battling a collapsing shelter.
Position your tent’s narrow end directly into prevailing winds to minimize exposed surface area. This reduces wind pressure by up to 60% compared to broadside positioning.
Point your tent’s narrow end into the wind to cut wind pressure by up to 60% versus sideways placement.
Proper tent alignment requires angling 27° to 45° diagonal to wind direction rather than facing it perpendicularly. This distributes wind loads more efficiently across the structure.
Match your tent’s orientation with terrain angles-align the narrow end with rising or falling slopes to reduce wind resistance.
Avoid positioning broad sides perpendicular to wind flow, which creates dangerous sail effects. Select sites below tree line when possible, as wind speeds increase considerably with elevation. Look for natural windbreaks such as rock formations, dense vegetation, or terrain features that can provide additional shelter from strong winds. Choose locations with good drainage to prevent water accumulation during storms that often accompany high winds. Consider tents with waterproof ratings between 3000-5000mm and sealed seams for optimal protection against the heavy rain that often accompanies strong winds.
Selecting Low-Profile Shelters for Maximum Stability
Beyond tent orientation, your shelter’s design fundamentally determines its ability to withstand severe weather conditions. Low-profile shelters reduce wind exposure by minimizing surface area directly impacted by gusts.
You’ll achieve maximum stability by selecting shelters with gently sloping panel shapes that allow wind to flow smoothly overhead, reducing dangerous uplift forces.
Hexagonal and octagonal designs offer superior wind resistance compared to rectangular A-frames. These multi-angled panel shapes break up wind flow and distribute forces across multiple points.
Conical shelters excel in extreme conditions because their rounded geometry lacks flat sides that create turbulence.
Choose shelter materials like 40D nylon with reinforced seams for durability without weight penalties.
Adjustable pole heights let you lower your shelter’s profile during storms, reducing its center of gravity and improving overall stability against wind-induced failure.
Advanced Guying Techniques and Anchor Points
Mastery of advanced guying techniques transforms your shelter from a vulnerable fabric structure into a wind-resistant fortress capable of weathering severe storms.
Multi point guying distributes wind forces across multiple anchor points, preventing catastrophic failure when gusts exceed single-line capacity. Your tensioning techniques must balance tautness with flexibility-over-tensioned lines create stress concentrators that tear fabric.
Critical Anchor Point Strategies:
- Stake at 45-degree angles toward your shelter to maximize ground holding strength under dynamic wind loads.
- Begin staking from the windward side to control tent positioning and prevent uplift during initial setup.
- Supplement stakes with natural anchors like rocks or logs for enhanced holding power in marginal soil conditions.
- Build snow walls windward of your tent to reduce direct wind pressure on guy lines and shelter structure.
Dynamic adjustment maintains peak performance as conditions change throughout the storm.
Strategic Setup Methods in Challenging Wind Conditions
While standard tent pitching works in calm conditions, windy environments demand a tactical approach that prioritizes shelter aerodynamics and structural integrity over convenience.
You’ll need to optimize tent orientation by positioning the narrowest profile into prevailing winds, reducing surface area exposure by up to 60%. This strategic placement minimizes wind catchment and prevents destabilization.
Lower your shelter’s profile by shortening poles and eliminating gaps between rain fly and ground. Choose aerodynamic designs with multiple guyline attachment points that distribute wind loads evenly.
Position doors away from wind direction to prevent internal pressure buildup.
Implement reinforced anchoring using 45-degree stake angles and fully tensioned guylines. Add weight to vulnerable points with rocks or sandbags.
Monitor conditions continuously and adjust accordingly. Wind resistance depends on methodical execution of these tactical setup principles.
For extended stays in harsh conditions, consider supplementing your shelter with a low-profile cot that maintains stability close to the ground while providing elevated comfort above cold or wet surfaces. A quality sleeping pad with built-in foot pump ensures quick setup without exhausting yourself in challenging wind conditions.
Smart Campsite Selection for Natural Wind Protection
Even perfect tent setup techniques won’t overcome a poorly chosen campsite when winds exceed 25 mph. Your location determines whether you’ll sleep comfortably or fight gusts all night.
Smart campsite selection requires identifying specific campsite features that naturally deflect wind. Dense vegetation types like willows and cottonwoods create effective barriers while reflecting radiant heat.
Position yourself downwind of these natural windbreaks for maximum protection.
Key selection criteria include:
- Woods, hills, or large boulders that provide established windbreaks
- Below treeline locations in alpine zones with krumholtz protection
- Natural ground contouring that shelters while maintaining drainage
- Stable tree clusters without deadfall or loose limb hazards
Just as ankle holsters require secure positioning for optimal function, your campsite needs strategic placement within natural terrain features for wind protection. Avoid exposed ridges, open plains, and wind corridors where speeds regularly exceed safe thresholds.
Consider wearing wind-resistant outer layers during campsite setup to maintain comfort and dexterity while working in gusty conditions.
Essential Maintenance and Safety Protocols
You’ll need to establish systematic inspection routines to maintain your campsite’s safety and functionality throughout your stay.
Regular checks of tent stakes, guy lines, and structural components prevent equipment failure during critical weather events, while emergency repair kits containing duct tape, spare stakes, and cordage enable immediate fixes when damage occurs.
These maintenance protocols serve as your primary defense against wind-related hazards that can compromise shelter integrity and camp safety.
Regular Inspection Protocols
Because campground safety directly impacts visitor welfare and regulatory compliance, establishing systematic inspection protocols forms the foundation of responsible facility management.
Your inspection schedules must align with state regulations requiring one to four annual inspections based on facility size. You’ll need thorough compliance documentation including current permits, licenses, and prior inspection records organized for immediate access.
Implement these essential protocols:
- Monthly self-inspections covering sanitation systems, restrooms, and waste disposal procedures
- Quarterly structural assessments examining tents, cabins, playground equipment, and emergency lighting systems
- Water quality testing following bacteriological monthly and chemical semiannual schedules
- Fire safety verification ensuring extinguisher accessibility, smoke detector functionality, and emergency exit clearance
Maintain detailed logs documenting cleaning schedules, maintenance activities, and corrective actions to demonstrate continuous compliance during regulatory reviews.
Emergency Repair Essentials
Emergency repairs at campsites demand immediate access to versatile tools and materials that can address multiple failure scenarios simultaneously.
Your repair toolkits should include a multi-tool combining knife, screwdriver, can opener, and scissors for diverse fixes. Duct tape serves triple duty: patching tent fabric, sealing food containers, and securing loose gear connections.
Tent pole repair sleeves restore broken poles without carrying bulky replacements. Pack extra paracord for guy line reinforcement and tarp securing.
Emergency supplies must include pad repair kits for maintaining sleeping insulation integrity. Keep zip ties for quick equipment fixes and bandanas for multipurpose applications. Store backup batteries for lighting devices and maintain fire extinguishers for flame control.
Consider adding neoprene construction materials to your emergency kit since they provide breathable, moisture-resistant properties essential for temporary shelter repairs in challenging weather conditions. Include seam-taped construction materials to maintain waterproof integrity when making emergency patches to tent walls or rainfly sections.
These essentials enable rapid response to equipment failures that could compromise your wind-resistant shelter system.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Wind Speeds Make Camping Unsafe and Require Shelter Evacuation?
You’ll need to evacuate your shelter when winds exceed 39-46 mph (Force 8). These wind speed thresholds represent critical camping safety guidelines where tent damage becomes inevitable and debris hazards threaten your safety.
How Do Different Tent Materials Perform in Sustained High Winds?
You’ll find polyester and DCF offer superior wind resistance compared to nylon’s flexibility. Canvas provides excellent stability in sustained winds, while nylon durability decreases under constant stress, making canvas stability your best choice.
Can Tarps or Emergency Shelters Substitute for Tents in Windy Conditions?
You can use tarps in windy conditions with proper rigging skills, but they’re less reliable than tents. Tarp advantages include lighter weight and versatility. Emergency shelters work temporarily but lack thorough wind protection.
How Does Altitude Affect Wind Intensity and Camping Strategies?
Higher altitude increases wind intensity due to reduced friction, requiring stronger guy lines and low-profile shelters. You’ll need altitude considerations for anchoring systems and must adapt to variable wind patterns above treeline.
On a final note
You’ve now mastered the fundamentals of wind-resistant camping. Your shelter’s survival depends on proper orientation, low-profile design selection, and strategic guying systems. Don’t compromise on anchor point strength-inadequate stakes fail at wind speeds exceeding 25 mph. Remember that natural windbreaks reduce exposure by 40-60%. Regular guy line tension checks prevent catastrophic failure. These techniques transform dangerous conditions into manageable situations, ensuring you’ll maintain camp integrity when others abandon their compromised setups.